Product Visualization 101
Why Sketching?
Embracing A 'Fail Fast' Mindset
The best products are born from numerous iterations. By embracing a hypothesis-driven approach and a ‘fail fast’ mindset, we create space for better solutions. Sketching and rapid prototyping are the quickest methods to facilitate design thinking and solicting feedback.
Based on the fidelity of the sketch, it can be categorized as an A sketch (thumbnail sketches), B sketch (advanced conceptual visualization), or C sketch (realistic rendering). — quote from Prof. Tony Kawanari.
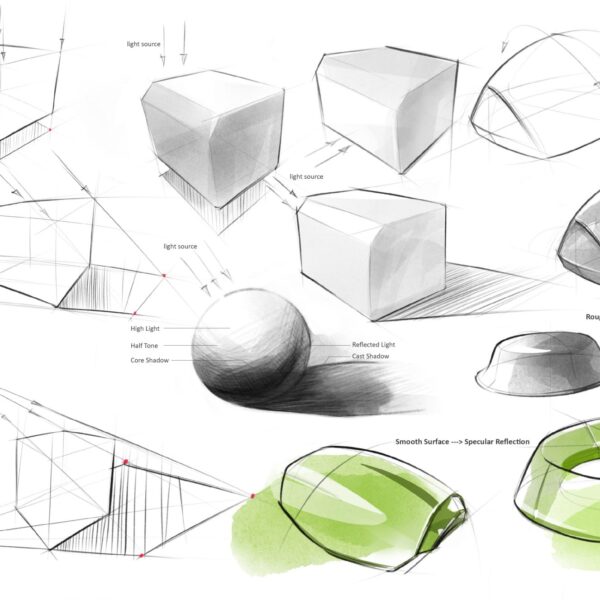
Type A Visualization
Thumbnails Sketch
small and explorative
Objective
These are also known as “Thumbnails”. This is the first step in the iterative design process, which are used primarily by the designer to quickly explore many ideas. A typical thumbnail takes anywhere between 10 seconds and 2 minutes to draw.
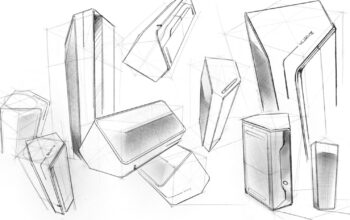
Type B Visualization
Advanced Conceptual Visualization
fleshed out and visual delibreation
Objective
Advanced conceptual visualization for your peer, client, management for first review. It shows through investigation and critical thinking. Based your audience, it could be investigative, explorative or explanaroty sketches. It leaves space for ambiguity and uncertainty.

Type C Visualization
Realistic Rendering
persuasive and artistic
Objective
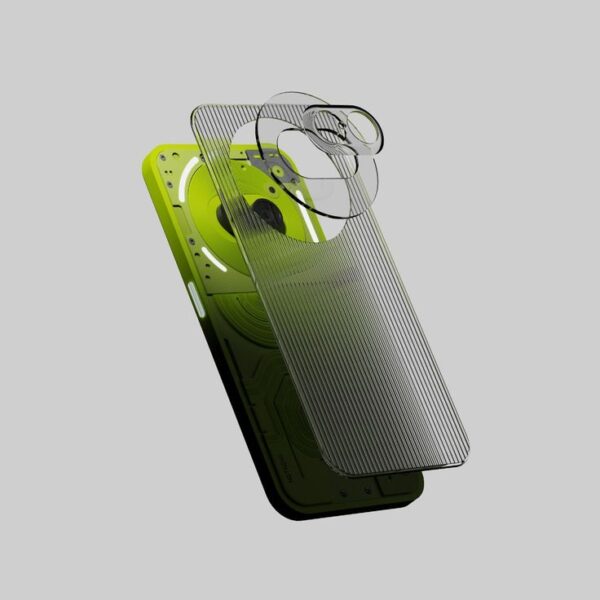
Comprehensive, refined delineation of concept.
Accurate in detail and color indication. It is used for final preliminary approval in lieu of form study model, communication model, presentation model. Use strong message to influence the audience.

Materials & Rendering
Type C Visualization
Both well-executed lineworks (Type A or B) and Type C rendering are good enough for communication. The only difference is the audience. Realistic rendering is used for client or management review. The other is used for internal peer review.
I personally prefer Type B sketching for communication. As a designer, we need to have ability to tolerance ambiguity during the iterative process.
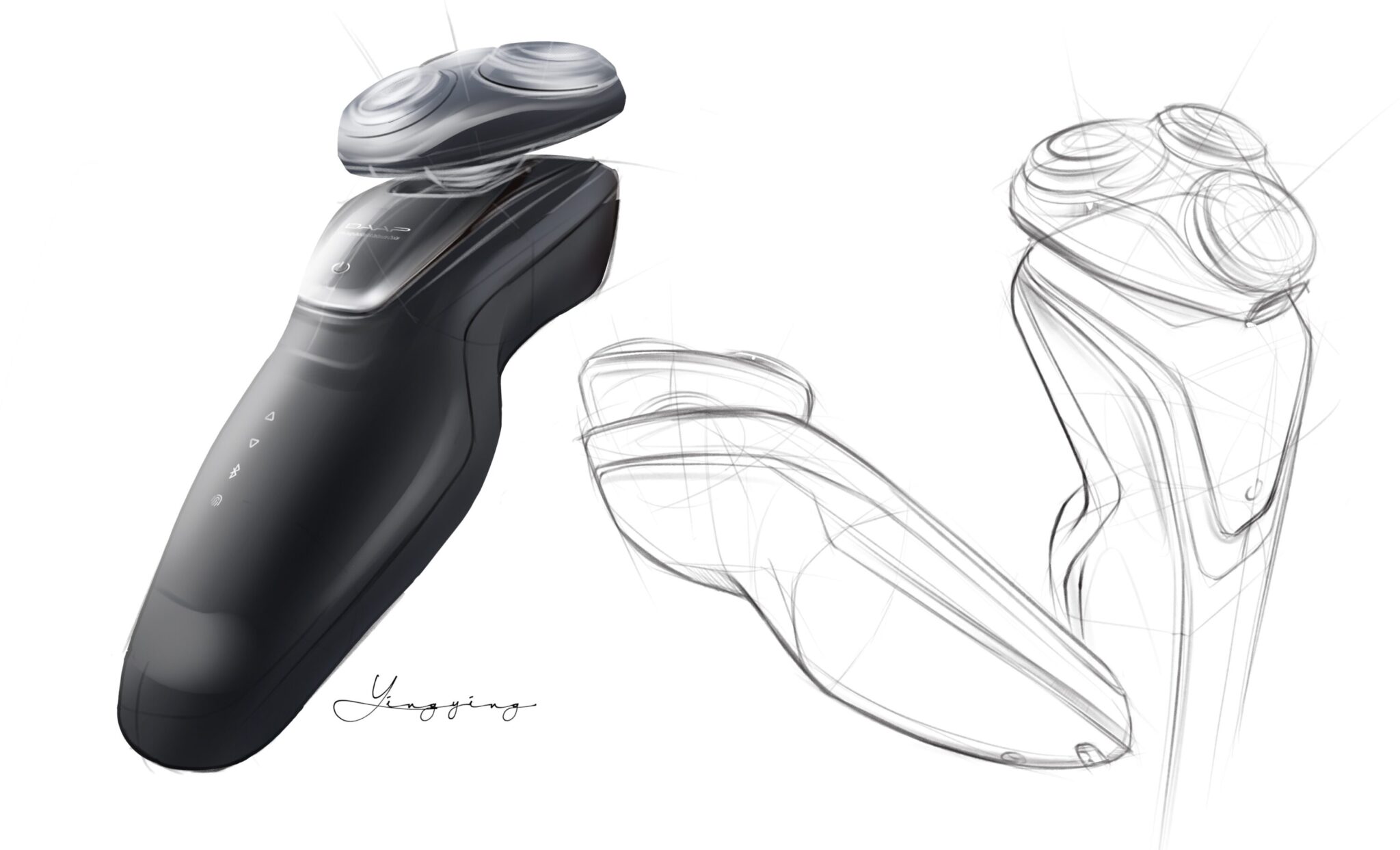
Watch the Timelapse Video here
Practice Makes Perfect
These Type C rendering demos are crafted by transitioning from 2D orthographic to 3D perspective rendering, progressing from simple geometric forms to organic forms, and exploring diffuse reflection to specular reflection. From introducing the artifact by elaborating on every detail to creating emotional storytelling through drawing. It also covers common CMF (Color, Material, Finish) choices.
The only way to improve is through consistent practice. Stress doesn’t come from hard work—it usually comes from not doing the things you actually have control over. Keep pushing forward!
Procreate Demos_ Please Find Step-by-step Demos Here.
Why Realistic Rendering?
Achieve Precise Visual Communication
Don't Let Your CAD Skill Define Your Design Ability
While AI-assisted rendering can accelerate the visualization process, it is critical to enhance foundational skills, including improving the quality of sketching and realistic rendering. These are the basic skills needed to take the lead and harness the power of AI in human-AI collaboration.
AI-assisted Visualization Process
Post Production (Procreate, more defined)
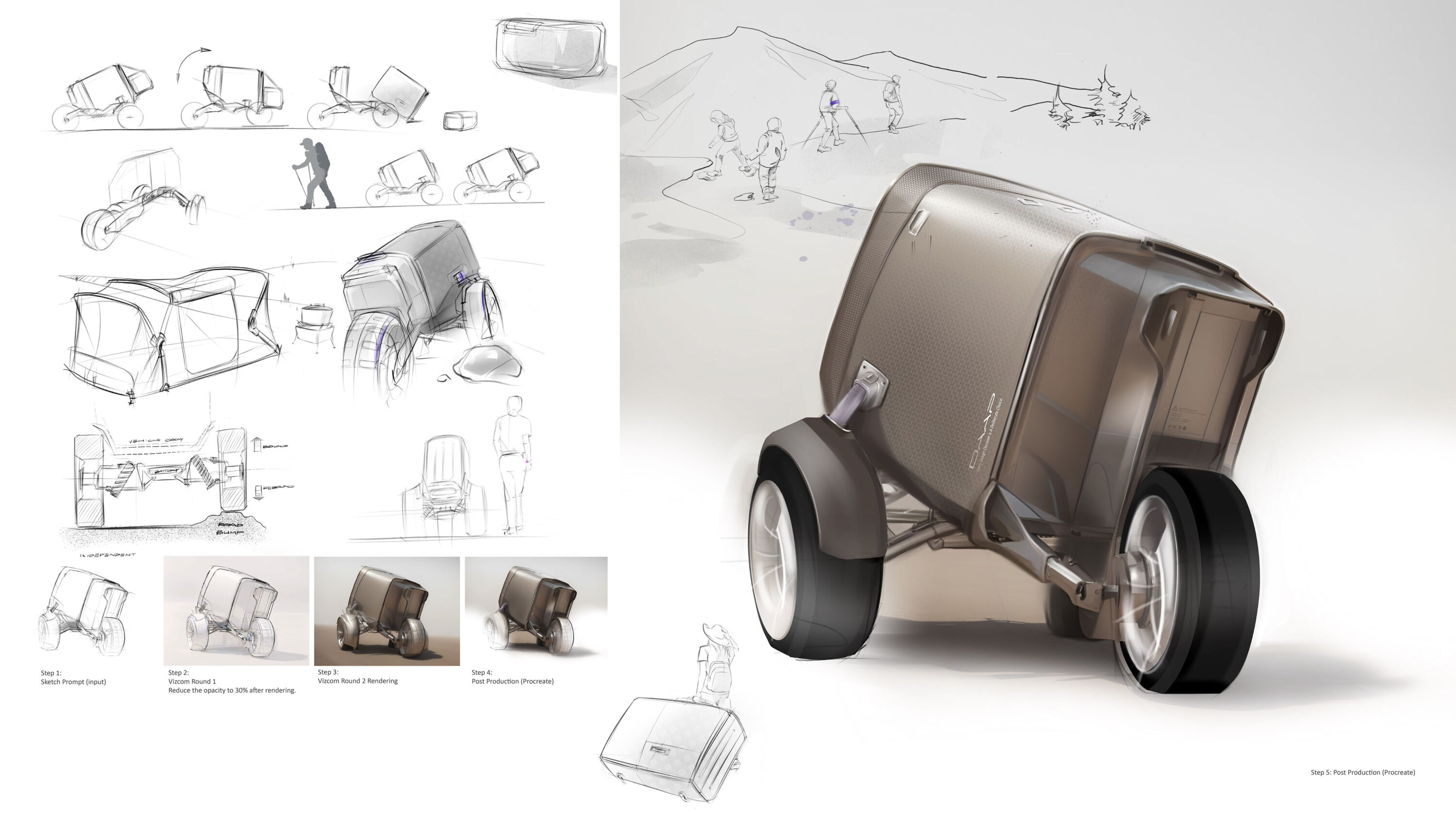
Sketching and Rendering Are More Than Just Skills,
It's About Communication and Iteration
Show your concept to others and solicit feedback for quick iteration. The goal of practicing realistic rendering is to train your eyes to see the sophicication of the surface and details. The ability to communicate effectively is crucial for taking the lead in human-AI collaboration.
Resource
Click images below for more information.